Lung Cancer
Screening for causes and symptoms of lung cancer for effective prevention and treatment to improve survival rate
Lung cancer is the deadliest cancer in Hong Kong, and most patients are smokers. Lung cancer has no obvious symptoms in the early stage and is usually detected only during other X-ray examinations for the chest. Patients who are diagnosed with lung cancer and receive treatment in the early stage will have a survival rate of 50% in the next five years. It is also important to prevent lung cancer by avoiding smoking or second-hand smoke.
Lung cancer is the most fatal tumor in Hong Kong. Among all malignant tumors, lung cancer ranked first in terms of the number of fatalities for all genders. According to the statistics, men are more likely to develop lung cancer than women. Lung cancer is usually caused by epidermal cell lesions in the bronchi and bronchioles. Lung tissue cells will grow uncontrollably, and without early detection, malignant tumors can even metastasize to adjacent tissues or other parts of the body. However, with early detection and treatment, patients who receive treatment in the early stage of lung cancer have a survival rate of 50% in the next five years. Therefore, in addition to avoiding smoking or second-hand smoke, regular body check-ups are also important.

Lung cancer is the number one killer among cancers and its survival rate is highly dependent on the timing of diagnosis and treatment. Research shows that if lung cancer is detected at stage I and treated immediately, the survival rate can be as high as 50% in the next five years, but if it is detected at stage III, the survival rate in the next five years drops to about 15%.
Symptoms of Lung Cancer
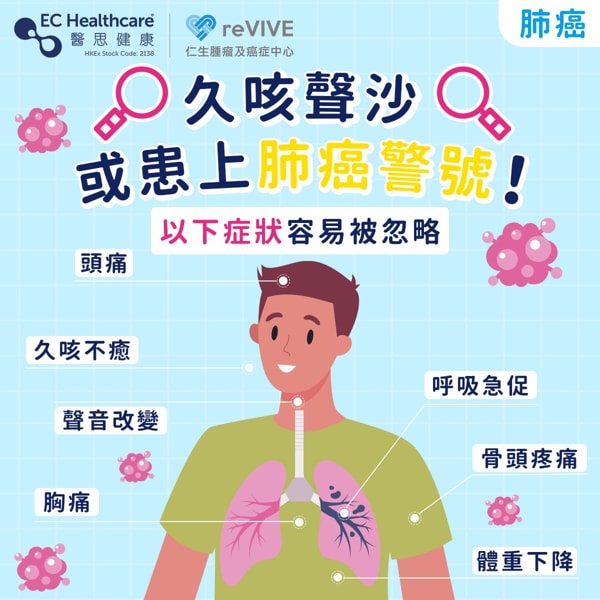
Lung cancer has no obvious symptoms in the early stage and is usually detected only during other X-ray examinations for the chest. As the condition worsens, lung cancer patients may experience the following symptoms:
- Shortness of breath
- Persistent cough
- Blood in the sputum
- Hoarseness: may be caused by cancer cells pressing the recurrent laryngeal nerve
- Difficulty in Swallowing
- Pain when taking deep breaths
- Repeated or chronic infection in the chest and lungs
- Loss of appetite
- Weight Loss
- Fatigue
In addition to the above symptoms, there are some less commonly noticed indicators, including:
- Increased thirst and frequent urination
- Clubbing of fingers or toes (enlargement and thickening of the fingertips or toes)
- Numbness or tingling in the shoulders or upper arms
- Unexplained hoarseness
- Swelling and discoloration of the upper body
- Horner's syndrome (drooping of the eyelids, smaller pupil size, reduced sweating on the affected side of the face)
If lung cancer has developed into an advanced stage, the cancer cells may spread. The patient may also experience symptoms such as swollen lymph nodes in the neck, abdominal distension, bone pain, headache, or swelling of the neck, face, and hands, or even partial epilepsy or hemiplegia. Therefore, if you experience the above symptoms, seek medical advice as soon as possible for a lung cancer diagnosis.
Causes of Lung Cancer
- Smoking
- Smoking is the main cause of lung cancer. The risk of lung cancer among smokers is 20 times higher than that of non-smokers, and up to 90% of male lung cancer patients are smokers.
- Second-hand smoke
- Second-hand smoke is also one of the causes of lung cancer. The risk of having lung cancer for people who constantly inhale second-hand smoke is two times higher than that of general people.
- Inhalation of chemical substances
- The long-term exposure to certain chemicals or construction materials, such as asbestos, nickel, uranium, etc.
- Long-term inhalation of cooking fumes
- Long-term inhalation of smoke from burning incense sticks
- Unhealthy diet
- The frequent consumption of grilled or marinated foods, and the inadequate consumption of vitamin A-rich foods, fresh vegetables and fruits.
- Hereditary factors
- Patients with parents or siblings diagnosed with lung cancer will have a higher risk of developing lung cancer than others.
Survival Rate of Lung Cancer

Screening and Diagnosis of Lung Cancer
Medical consultation:
Medical History (e.g. gynaecological disease, obstetric history), allergies, family medical history, plans for pregnancy and contraception methods, menstrual cycle, etc.
Physical examination:
Measure height, weight, blood pressure, check for anaemia and thyroid disease.
Chest X-ray:
The examination is the most basic method for detecting lung cancer and assessing the condition of the lungs. If any abnormalities are detected on the X-ray, further testing can be arranged. However, lesions smaller than 1 cm can be difficult to detect and interpret.
CT scan:
It is one of the most effective ways to detect lung cancer, providing more detailed images than a chest X-ray. It can detect tumors smaller than 0.3 cm and help doctors determine the stage of cancer.
MRI:
Similar to CT scanning, it provides detailed soft tissue images, but it uses radio waves and strong magnetic fields instead of X-rays. It is often used to check whether cancer cells have spread to the brain or spinal cord.
The earlier detection of lung cancer brings a higher chance of recovery. Therefore, smokers or frequent passive smokers should have regular check-ups and stay vigilant. If you suspect any symptoms of lung cancer, you should seek medical advice and examination.
- Chest X-ray: Observe any tumours or other abnormal substances in the lungs
- Sputum cytology: Use a microscope to observe the presence of cancer cells in the sputum
- Bronchoscopy: Examine the mucous membrane in the bronchi, and extract tissues for pathological examination to examine the type of cancer cells
Diagnosis of Lung Cancer
After the initial examination, the doctor may request further cancer tests such as mediastinoscopy, computerised tomography (CT scan) and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS). These tests facilitate the precise classification of the types and stages of the patient’s lung cancer.
- Mediastinoscopy
The patient is put under general anaesthesia to make two to three small incisions at the bottom of the neck and on the top of the breastbone. An endoscope is inserted to observe the lymph nodes and thymus glands surrounding the lungs and heart.
- Computed Tomography (CT Scan)
The patient will be injected with a contrast agent before the scan. Then a CT scan will be used to take X-ray images of body tissues from different angles to form a 3D picture.
- Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)
A soft tube with an ultrasound transducer is inserted into the patient's oesophagus through the mouth. The rebounding sound waves from the heart and lungs will be visualized by the computer to observe if the lymph nodes in the chest cavity are swollen.
There are three types of lung cancer:
- Small cell lung cancer
- This type of cancer develops from the smallest cell of the lung, usually the one in the bronchial wall. Cancer worsens with the rapid spread of cancer cells to other parts of the body in the early stage, making it difficult to cure.
- Non-small cell lung cancer
- Squamous cell carcinoma: It is commonly found in the tracheal wall and is usually caused by smoking
- Adenocarcinoma: It is caused by the abnormal growth of the mucus-secreting cells in the trachea wall and affects mainly the outer lung.
- Large cell carcinoma: involves larger and rounder cancer cells.
- Carcinoid (neuroendocrine tumour)

Treatment of Lung Cancer
The five major treatments for lung cancer include: surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, targeted therapy and immunotherapy. They can be used alone or in combination with other palliative treatments, depending on the patient’s condition.
- Surgery
The surgeon will assess the condition of the patient and determine the most suitable type of surgery: removal of a lobe of one lung (lobectomy), removal of two lobes (bi-lobectomy), or the entire lung (pneumonectomy). The surgeon will make a cut on the patient’s chest, and insert a thoracoscope into the chest cavity to minimize the incision and scar while reducing post-operative pain. Surgical treatment can also be used alone or in combination with other palliative methods, depending on the patient's condition.
- Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy, also known as “Chemo”, uses an intravenous injection to inject cytotoxic drugs through the bloodstream to kill the cancer cells by blocking their growth and division.
- Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy uses high-energy ray beams to target and kill the cancer cells. It can be used for the radical treatment of early-stage lung cancer. and locally advanced tumors, as well as eradicating any remaining cancer cells after surgery. Radiotherapy is also indicated for patients who cannot undergo surgery due to old age and other illnesses.
- Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy is designed to target certain cancer cells and has fewer side effects than general chemotherapy. It is suitable for patients with advanced lung cancer. Lung cancer has the most developed target therapy among all tumors, with about ten types of genetic mutations capable of matching with their corresponding targeted drug. The use of targeted therapy as precision medicine demonstrates a high response rate of tumor shrinkage, as well as insignificant side effects compared with chemotherapy.
- Immunotherapy
It is designed for patients with intermediate to advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Some advanced cancer patients with a high level of PD-L1can even be treated with immunotherapy alone without chemotherapy. For some patients with non-metastatic stage III tumors which cannot be surgically removed, immunotherapy can be used as consolidation therapy after combining chemotherapy and radiotherapy to help reduce the risk of recurrence.

Recovery and Rehabilitation of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer has a high recurrence rate, therefore patients are advised to have regular follow-up consultation during their recovery so that they can receive timely treatment in case of recurrence.
In addition, patients have to pay attention to their daily diet and adopt a balanced diet. If patients have any other chronic diseases or dietary concerns, seek medical advice from doctors. Adequate hydration can reduce mucus viscosity and facilitate coughing up the sputum.
Patients should also maintain a regular lifestyle and a pleasant mind. Proper rest and adequate sleep can help relieve stress and promote recovery after the surgery. Keep the house well-ventilated and avoid going to crowded places with turbid air to help prevent respiratory infections. Adequate exercise can also enhance lung function and foster recovery.
Most importantly, patients must quit smoking and avoid inhaling second-hand smoke to better let their lungs recuperate.
Prevention of Lung Cancer
Act now to prevent lung cancer. Avoid bad habits and have regular medical check-ups to protect your health.
Non-smokers should stay away from bad habits, while smokers should quit smoking as soon as possible. You should avoid second-hand smoke and go to places where many people smoke. Avoid going to popular smoking areas with a high chance of inhaling second-hand smoke.
As for hazardous substances, you should be alert and test your residence for the presence of hazardous substances such as asbestos. Employees should also follow safety guidelines and wear protective masks in their workplaces.
In addition, you can adopt a diet with more fruits and vegetables to maintain a healthy body. Regular health check-ups are necessary to identify illnesses and abnormalities in body functions, and facilitate follow-up treatments for effective prevention.
Lung Cancer FAQ
Q: Is lung cancer hereditary?
The genetic mutations associated with lung cancer are usually acquired during a person's lifetime and are not hereditary. Acquired mutations in lung cells are usually caused by exposure to factors in the environment, such as carcinogenic chemicals in tobacco smoke.
Q. Is it possible to have lung cancer without the symptoms of coughing?
Shortness of breath and wheezing may also be the early signs of lung cancer. In addition to shortness of breath, some people may have a mild cough. Others may have difficulty in breathing but no cough.
Q: What age group is the most affected by lung cancer?
Lung cancer mainly occurs in older people. Most people diagnosed with lung cancer are 65 years old or above; only an extremely small number of diagnosed patients are below 45 years old. The average age of diagnosed patients is about 70 years old.



